.NET Core 实战 [No.232] 使用并行 LINQ
开启 LINQ 查询的并行模式,只需在原序列上调用 AsParallel 扩展方法,但是不应该滥用并行模式。
满足以下条件的查询,可以考虑以并行模式执行:
- 序列中数据量很大
- LINQ 查询中
where与select子句上需要额外的处理工作(例如要转换类型) - 对产生的结果没有严格的顺序要求(尽管并行查询可以调用 AsOrdered 扩展方法来维持序列的顺序,但在一定程度上会降低性能,仅在必要时使用)
示例代码
定义一个结构 Rectangle 。
csharp
public struct Rectangle
{
public double Width;
public double Height;
}初始化一个 ConcurrentQueue<Rectangle> 集合,然后使用两种模式执行 LINQ 查询,计算矩形的面积。
csharp
var testList = new ConcurrentQueue<Rectangle>();
Parallel.For(20, 300000000, n =>
{
testList.Enqueue(new Rectangle()
{
Width = n,
Height = n,
});
});
Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch();
watch.Restart();
var q1 = from x in testList
select x.Width * x.Height;
watch.Stop();
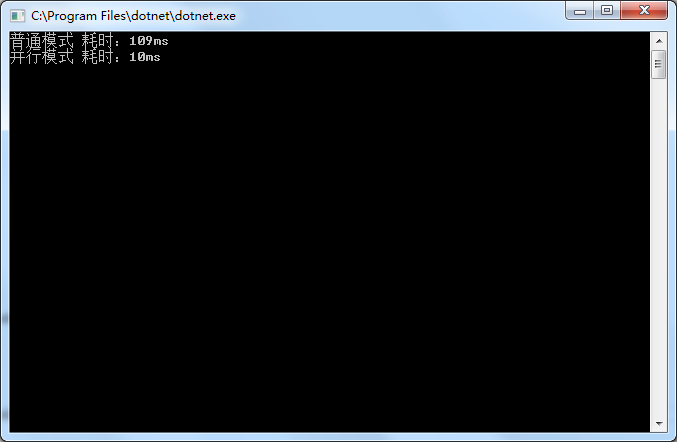
Console.WriteLine($"普通模式 耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");
watch.Restart();
var q2 = from x in testList.AsParallel()
select x.Width * x.Height;
watch.Stop();
Console.WriteLine($"并行模式 耗时:{watch.ElapsedMilliseconds}ms");从输出结果看,并行模式下执行 LINQ 查询提升了性能。
注意
Stopwatch 组件自身在运行期间也会占用一定的 CPU 资源,因此该组件所统计的耗时并非完全准确,仅供参考。
参考:《.NET Core 实战:手把手教你掌握 380 个精彩案例》 -- 周家安 著
